

Our understanding of the cardiovascular (CV), renal and metabolic diseases (MD) has significantly improved over the last ten years due to better knowledge of interplay between CV and MD conditions. Both CV and MD manifest often in combination of associated complications leading to array of physiological complications. Thus, requiring a clear understanding of each disease conditions and therapeutic interventions in a clinically relevant animal model.
Globally, CV disease is a major cause of human mortality due to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and diabetes. Therefore, it is vital to explore the interlinked CV, renal and metabolic diseases. A critical need is to manage all CVMD rather than treating each condition in isolation. Leading pharmaceuticals are perusing science to understand the underlying connection between the heart, kidney, and pancreas, and how the drug or drugs in combinations slow disease progression, reduce mortality and co-morbidities in patients with Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases (CVMD).
The two major underlying causes of CVMD are disorders of lipid metabolism, and metabolic syndrome that includes high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high fat, and abnormal cholesterol. Aragen continually strives to work with its client and partners in developing clinically relevant preclinical animal models that closely mimic the human disease condition for with IND-enabling studies. Thus, we help you to advance ameliorative or therapeutic treatment development.
Developed in male C57BL/6 mice of 40-45g fed with 60% Kcal HFD (D12492, Research Diets), Rimonabant, GO-CoA-Tat (Peptide) .
Key Features:
Readouts:
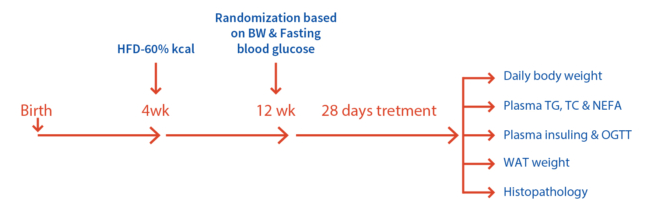
Case study: Body weight measured in mice (5 weeks old) fed with HFD compared to mice fed with normal chow
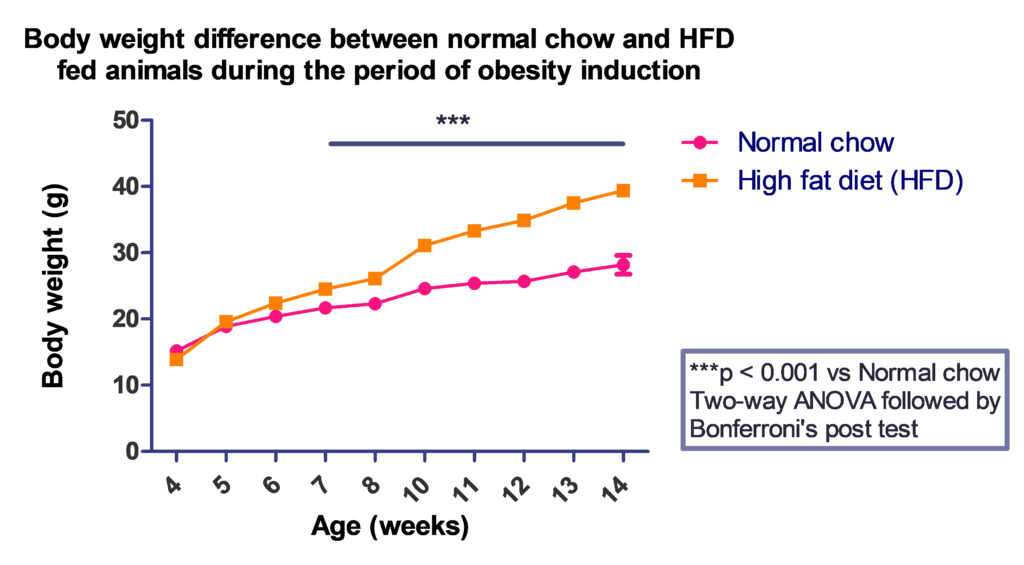
HFD fed group showed significant weight gain as compared with normal chow fed group.
Case Studies:
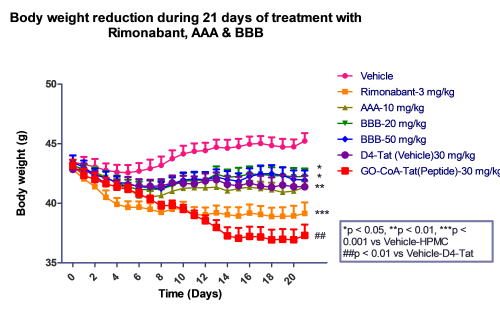
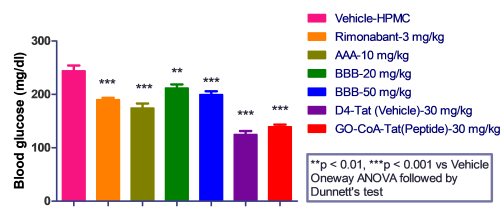
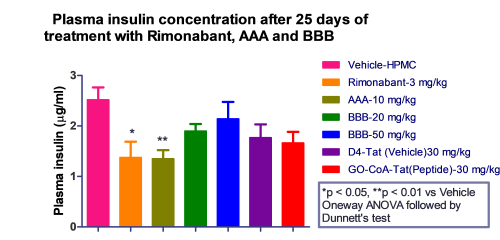
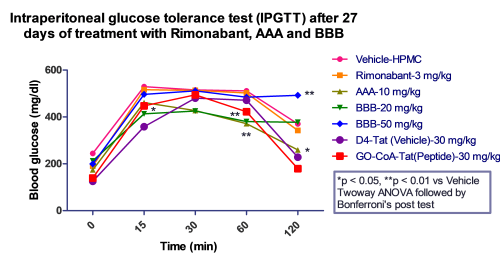
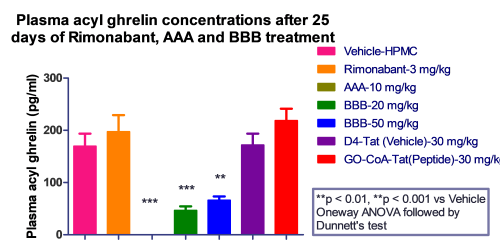
We observed that Rimonabant along with all the test compounds exhibited significant reduction in body weight of mice compared to HFD fed mice.
Key Features of Model:
Readouts:
Effect of treatment (test compound) studied in Acute Dyslipidemia Mouse model
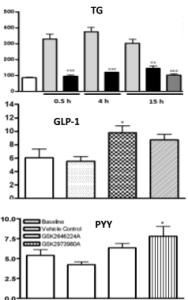
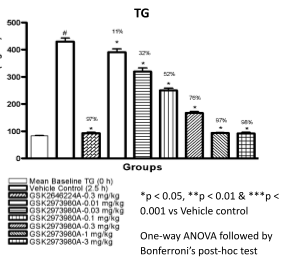
The test compound showed dose response and time course effect on plasma triglyceride levels, and significantly increased the plasma levels of active GLP-1 and PYY as shown in the bar diagrams above.
Key Features: Translational model for human diseases like fatty liver, MASH and HCC created by combination of chemical, streptozotocin (STZ) (Post-natal day 2) and high fat diet (HFD, 60% kcal) (from 4 weeks till end of the treatment)
Mice: Male C57BL/6 mice, Body weight: 20-25g
Drugs Tested: Elafibranor (Dual agonist of PPAR α and δ), Obeticholic acid (OCA) (FXR agonist) and Telmisartan
Readouts: Daily body weight; Food intake (Twice weekly)
Biochemical- Fasting blood glucose; ALT and AST levels
Histopathological – H&E (Inflammation, steatosis & degeneration); Oil-Red-O (Steatosis marker); Masson’s trichrome (Fibrosis marker)
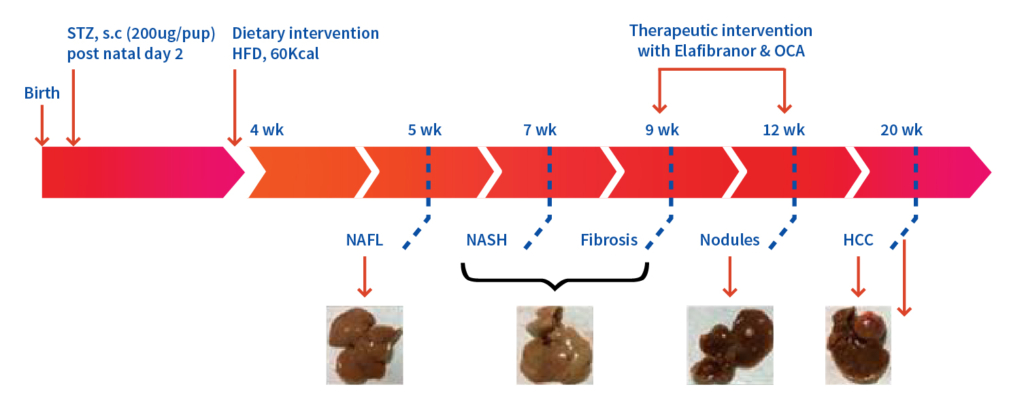
Case Study: Elafibranor and Obeticholic acid evaluated in STZ-HFD-Induced Mouse Model
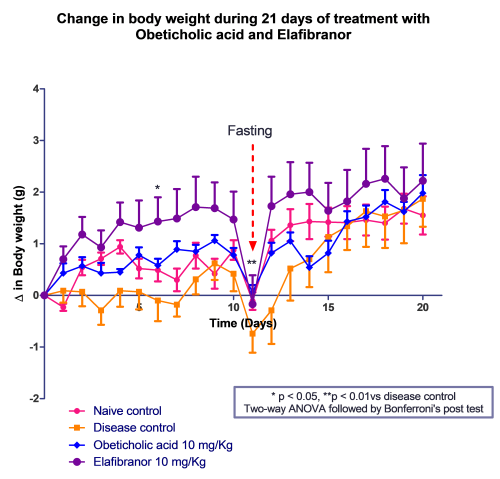
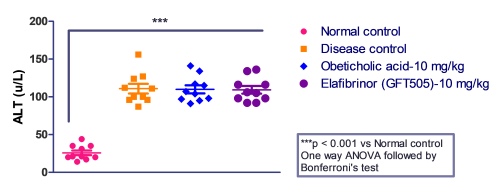
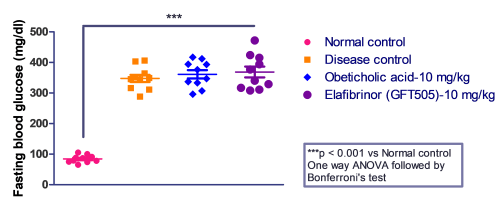
Fasting blood glucose and serum transaminase (ALT and AST) were measured to qualify MASH before the before the initiation of the treatment.
Mice administered with Elafibranor gained most weight over 21 days followed by Obeticholic acid -treated mice as compared with vehicle control. The mice were fasted overnight on day 11 midterm to measure blood glucose levels.
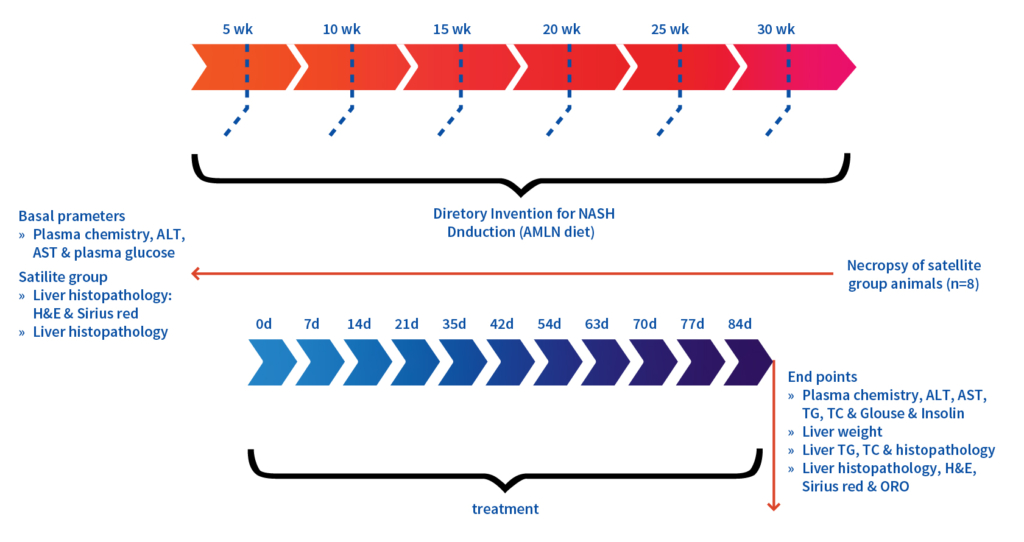
Study Design
Key Features:
Male C57BL/6 mice (5-6 weeks) developed a translational human MASH disease model in 30 weeks after feeding them with high fat diet (AMLN diet, 40 kcal% (mostly palm oil),
20 kcal% fructose and 2% cholesterol; D09100310)
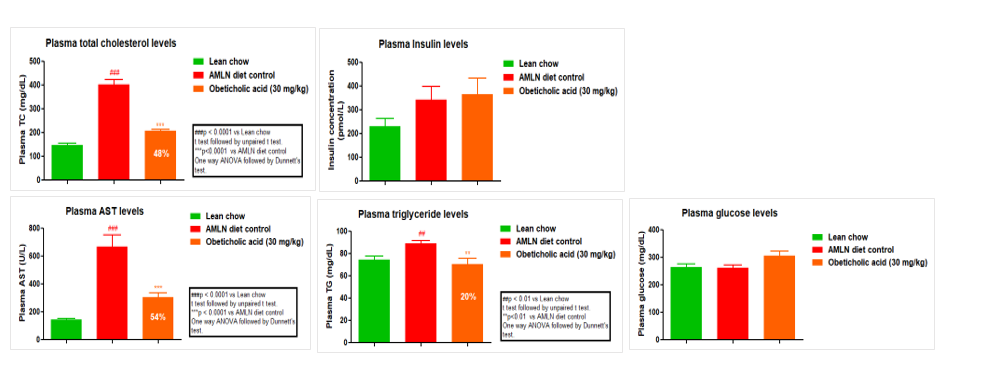
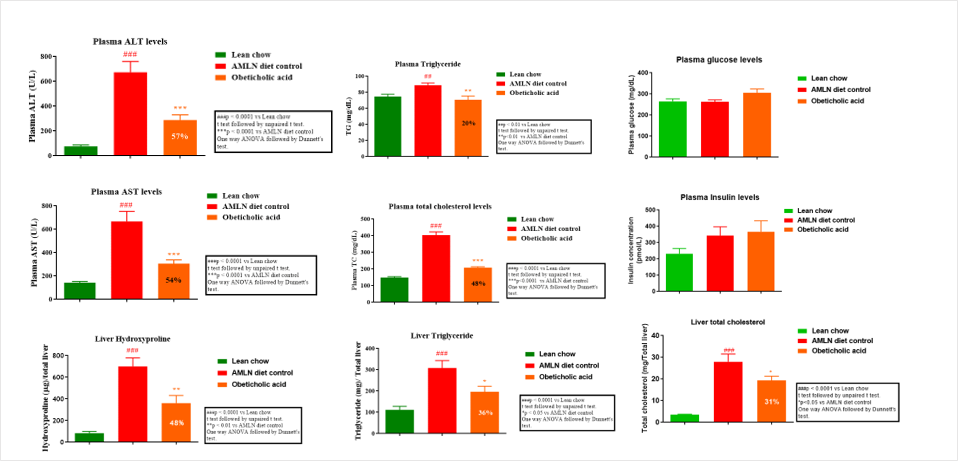
Treatment Intervention:
Obeticholic acid for 84 days
Case study: Measurement of Physical parameters in AMLN fed animals and in normal chow -fed controls.
A significant body weight gain was observed in AMLN fed animals as compared normal chow-fed mice. AMLN-fed mice had significant increase in ALT and AST levels as compared with normal chow-fed mice. We also observed a slight but not significant increase in plasma glucose and liver/BW ratio in AMLN-fed group as compared with normal chow-fed group.
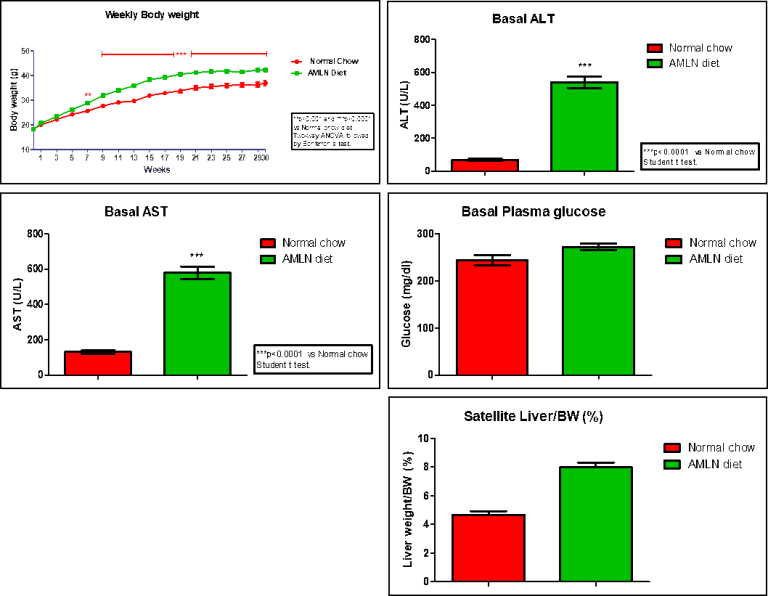
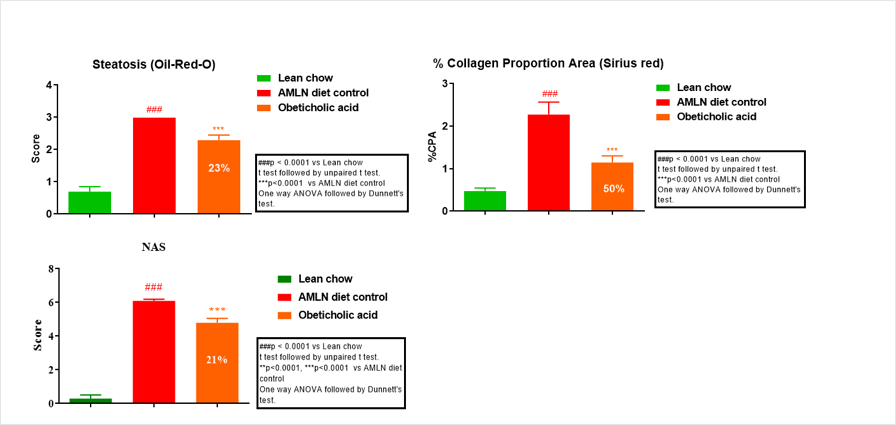
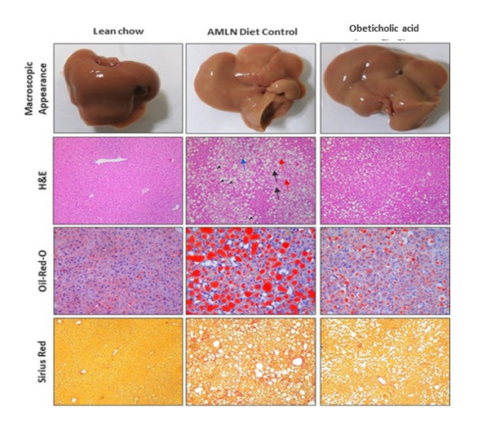
Disease Induction Results in AMLN MASH Mouse Model
AMLN fed animal livers showed high levels of collagen deposition as depicted by Sirius red staining and high levels of lipid accumulation as depicted by ORO staining.
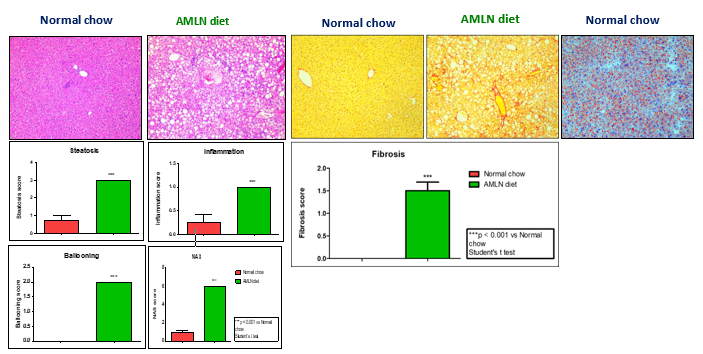
Immunohistochemistry study- ER-TR7 expression in hepatic tissue
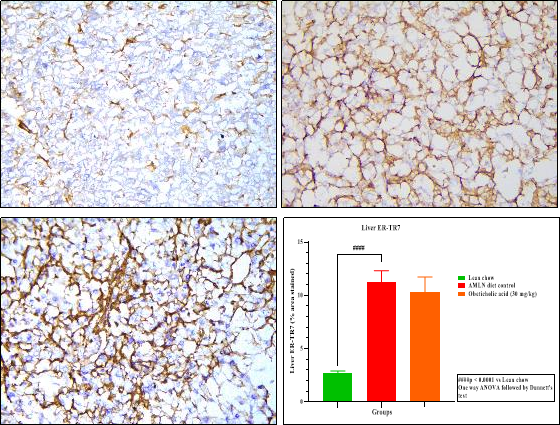
The AMLN diet-fed mice had significantly increased of ER-TR7 in hepatic tissue section as well as increased deposition of reticular fibroblasts as compared to lean chow-fed mice. However, OCA treatment did not result in any significant decrease in reticular fibroblasts deposition.
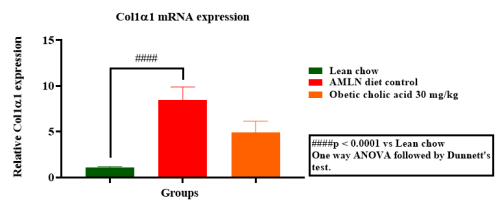
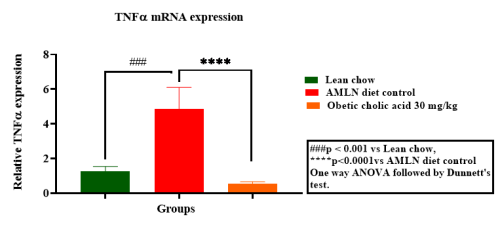
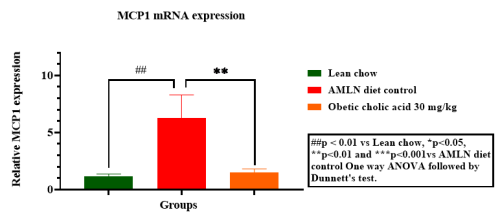
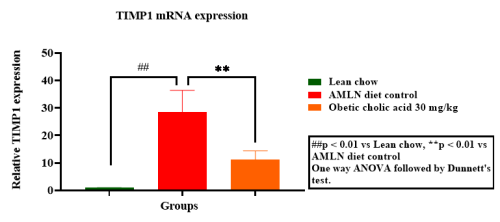
Hepatic gene expression of Col1a1, TNF-α, MCP1 & TIMP1
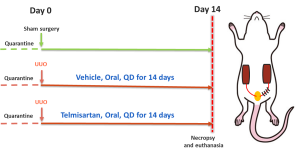
Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction (UUO), a model for studying Renal Interstitial fibrosis
Key Feature:
Model development:
Male C57BL/6 mice (20-25 g) treate4d with Telmisartan for 14 days
Readouts:
Case study: Tubular dilations measured in Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction (UUO) model of Renal Interstitial Fibrosis and H&E staining on Kidney tissue
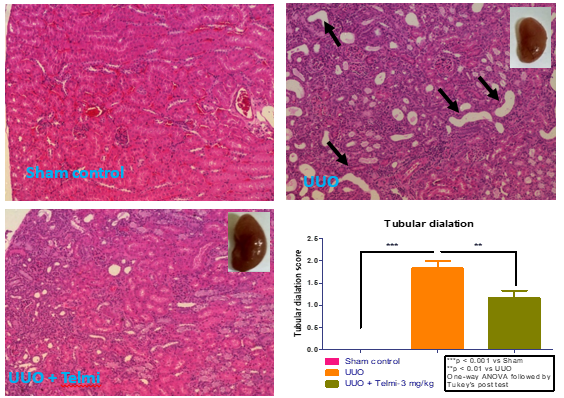
Histograms show a marked increase in number of tubular dilations (arrows) at day 14 following UUO, which was reduced following Telmisartan treatment as compared to control group.
Bar graph: Scoring done using the following criteria: 0 = affecting 0-5% of the renal area, 1 = affecting 6-25%, 2 = affecting 26-50% of the renal area, 3 = affecting >50% of the renal area
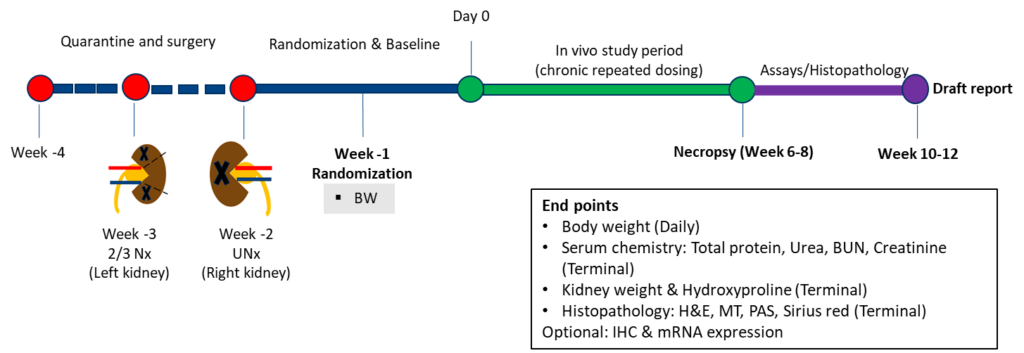
5/6 nephrectomy (5/6 Nx)
Key Benefits
Model
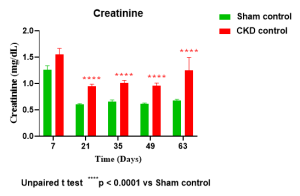
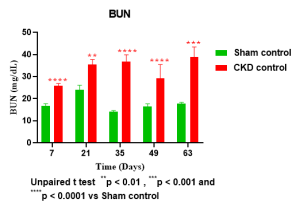
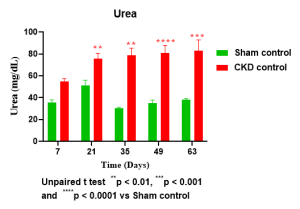
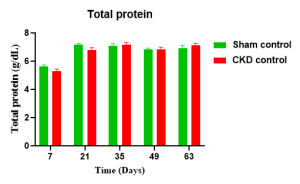
Case study: Serum chemistry in rats subjected to 5/6 nephrectomy (5/6 Nx)
Histopathology (H&E) with Sirus Red of kidney tissue in rats with 5/6 nephrectomy (5/6 Nx)
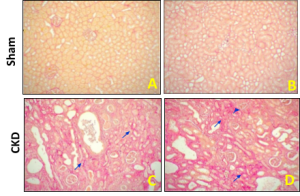
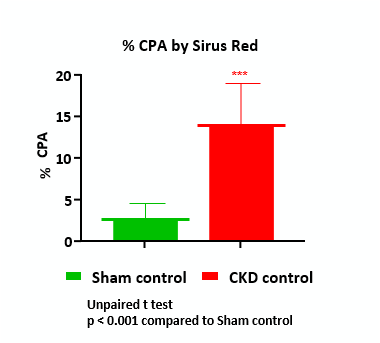
Normal kidney Sirius red within normal limits or no fibrosis (A & B). The CKD control animal’s kidney Sirius red images show slight (blue arrowhead) and marked interstitial fibrosis (blue arrow, C & D)
Case study: Dabigatran and Enoxaparin- induced rat tail bleeding Model
Key Features
Readout
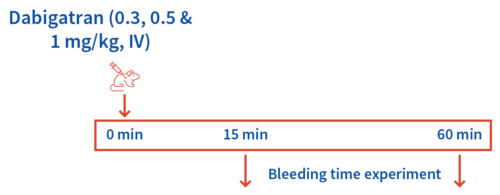

Case study: Dabigatran at 0.5 mg/kg showed ~4-fold increase in bleeding time in 15 minutes post dabigatran administration
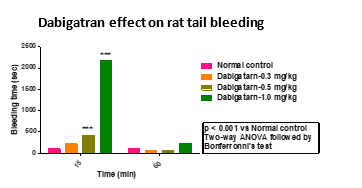
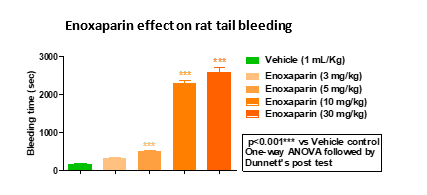
The Dabigatran (Dose-3) administration increased the bleeding time to 2173.40 sec (20-fold). The Enoxaparin (Dose-1, Dose-2 and Dose-3) administration significantly increased (3.0, 13.3, and 15.0-fold, respectively) bleeding time post 5 min Enoxaparin administration. However, lower doses of Dabigatran (Dose-1) & Enoxaparin (Dose-1) did not increase the bleeding time significantly as compared to vehicle control.
Case Study: Monocrotaline (MCT) – induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) in Male SD Rats.
Model Development: We injected male SD Rats (220±30g) on day 0, subcutaneously with MCT (50 mg/kg). The reference compounds were Sildenafil (10, 30 & 100 mg/kg) and Macitentan (10, 30 & 100 mg/kg; per oral; QD for 14 days).
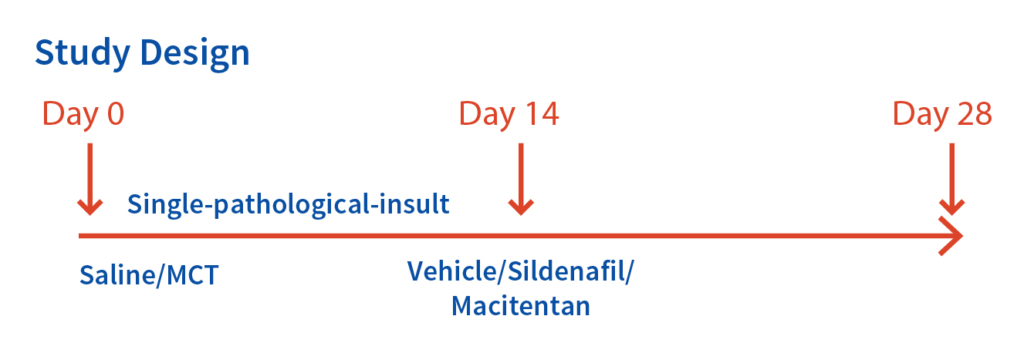
Key Features
Readouts
Case Study: Measuring Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) in Rats
Representative Hemodynamic parameters – Right Ventricular Pressure (RVP), Representative Tracings
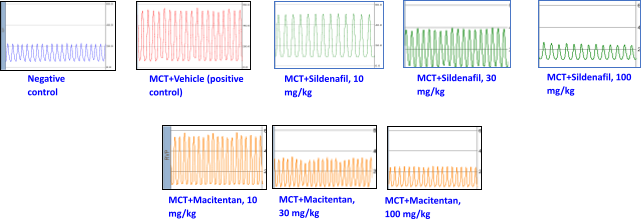
MCT administration significantly elevated right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) & right ventricular pressure (RVP). The Sildenafil and Macitentan administration reduced RVSP & RVP in a dose dependent manner.
