

Phosphoramidite chemistry is the industry standard for synthesizing siRNA, DNA and RNA oligonucleotides. It employs a modular approach, introducing each nucleotide as a phosphoramidite building block for precise sequence assembly. This method integrates seamlessly with automated systems, supporting small scale, large-scale and high-throughput synthesis possible with coupling efficiencies typically exceeding 99% per step. Its versatility allows incorporation of modified bases and functional groups, essential for therapeutic and diagnostic applications, while scalability suits both research and industrial production.
CRDMOs, like Aragen advance this chemistry through integrated route scouting, validation, and automated synthesis, ensuring quality and cost-efficient scale-ups for discovery solutions.
This whitepaper details phosphoramidite chemistry principles and route scouting highlighting how Aragen’s expertise enables innovation, accelerates development timelines, and ensures a reliable supply of high-quality oligonucleotides for therapeutics, diagnostics, and research and development.
Oligonucleotides—short, sequence-defined DNA or RNA molecules—are vital in gene modulation, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications. Growing demand for high-purity, chemically modified oligonucleotides requires synthesis platforms that provide precision, reproducibility, and flexibility across research and industrial environments. Phosphoramidite chemistry remains the backbone of this capability.
Principles of Phosphoramidite Chemistry
Phosphoramidite chemistry involves stepwise addition of nucleoside phosphoramidite to a growing oligonucleotide chain anchored on a solid support. Each cycle involves four key steps: deprotection of the 5′-hydroxyl group, coupling of the activated phosphoramidite with the free hydroxyl, capping of unreacted sites to prevent errors, and oxidation to convert the phosphite triester into a stable phosphate linkage. This highly efficient and modular process enables precise, automated synthesis of DNA and RNA sequences with high coupling yields and flexibility for chemical modifications, delivering high coupling efficiencies, ensuring precise sequence length, purity, and chemical uniformity across scales.
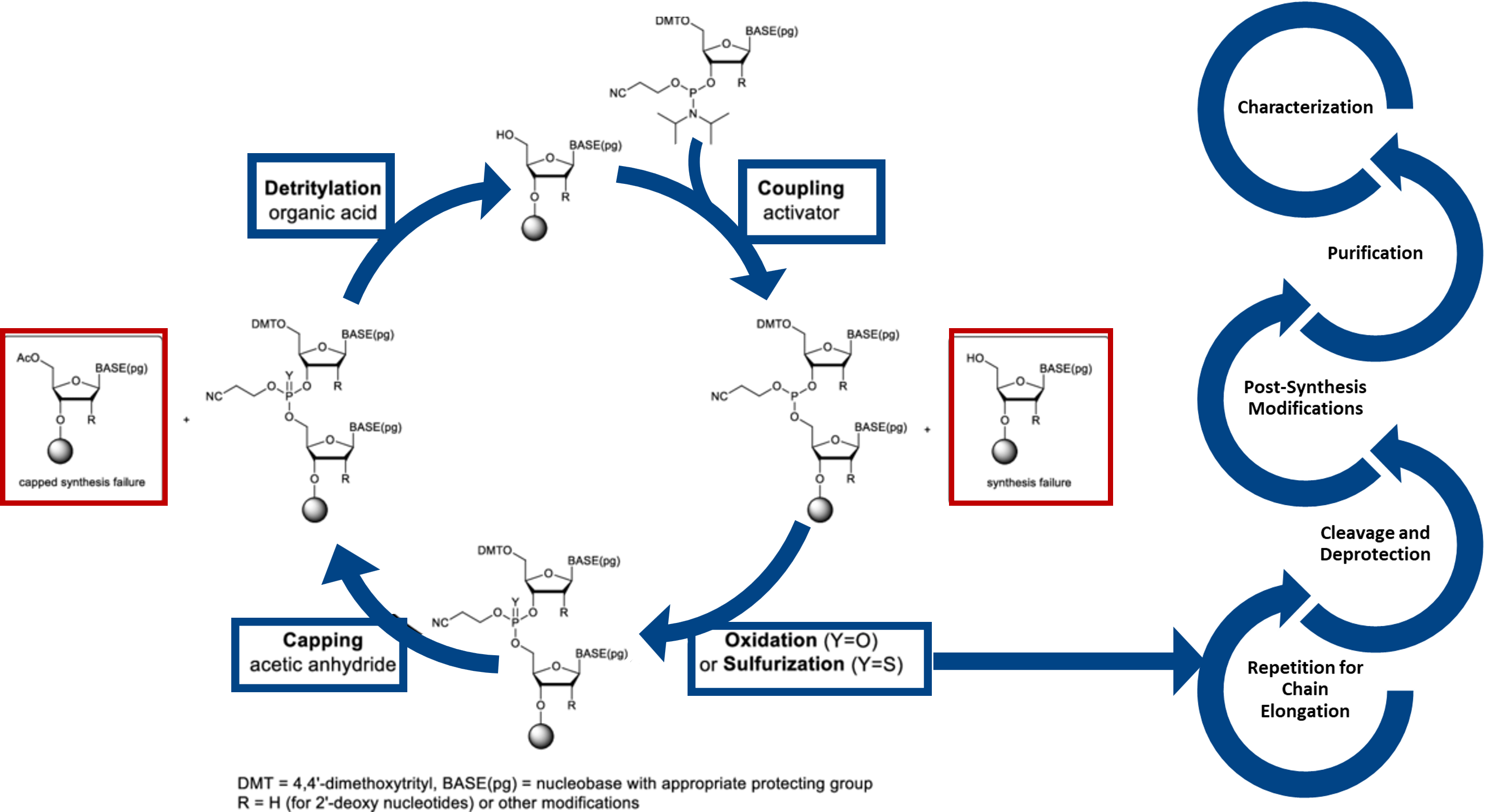
Figure 1: The phosphoramidite-based oligonucleotide synthesis cycle adopted at Aragen. (Adapted from Gao, et. al., 2025. Enzymatic de novo oligonucleotide synthesis: Emerging techniques and advancements. Biotechnology Advances, 108604).
Incorporation of Modifications in Phosphoramidite Chemistry
Phosphoramidite chemistry is the standard method for synthesizing oligonucleotides on a solid support. Modified nucleosides are introduced as phosphoramidite derivatives, enabling incorporation of chemical changes at the base, sugar, or phosphate backbone. Common modifications include:
The phosphoramidite approach is uniquely adaptable to these modifications since each building block can be chemically engineered for synthesis compatibility. Consequently, service providers must demonstrate capability in:
Automated synthesizers streamline phosphoramidite chemistry by enabling parallel processing, precise control over reaction cycles, and real-time quality monitoring. These platforms reduce synthesis times, minimize reagent waste, and support diverse modifications, allowing customers to obtain consistent, high-purity oligonucleotides rapidly for iterative R&D and early-stage validation.
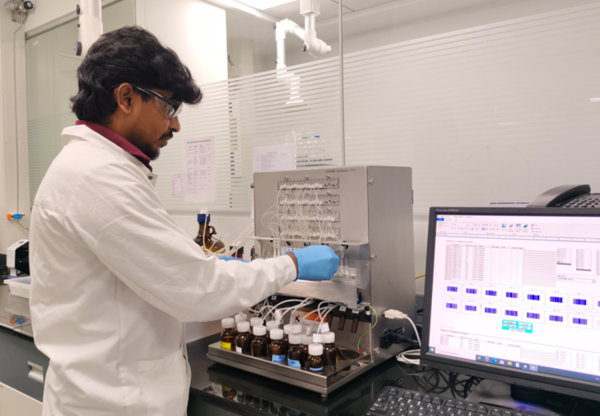

Figure 2: Automated oligonucleotide synthesizer (K&A H-16) in Aragen’s laboratory.
Aragen employs the K&A H-16, a 16-column synthesizer (Figure 2) designed for high-purity DNA, RNA, and LNA production with low reagent use and rapid cycle times (for DNA 5-6 mins and for RNA 25-30 mins) per 16 columns. Key capabilities include online trityl monitoring across all columns for real-time quality control, flexible scales from 5 nmol to 10 µmol per column, support for wobbles or mixed bases, and programmable control to start new syntheses independently, ensuring efficient handling of complex modifications like phosphorothioates while delivering reproducible results up to 200 mers.
Post-synthesis purification eliminates failure sequences, residual protecting groups, and byproducts, achieving purity levels essential for downstream applications—typically >90% for research and higher for therapeutics. Method selection optimizes resolution, throughput, and compatibility with modifications, helping customers meet performance specs efficiently without excessive processing costs. Aragen provides tailored options based on oligonucleotide properties and project needs (Table 1).
Table 1: Comparison of oligonucleotide purification methods offered by Aragen.
| Method | Principle | Pros | Cons | Best use case |
| Cartridge (RP) | Reverse-phase (C18) adsorption | Fast, low cost, simple | Limited resolution for long/modified oligonucleotides | Quick post-synthesis cleanup |
| Reverse-Phase HPLC | Hydrophobicity separation (trityl-on/off) | High resolution, scalable | Requires instrumentation, solvents | Research-grade oligonucleotides, modified bases |
| Ion-Exchange HPLC | Charge-based separation | Excellent for charged modifications | Complex setup, longer runtime | Highly modified or charged oligos |
| PAGE | Size-based separation | Very high purity for short oligos | Labor-intensive, not scalable | Analytical or structural studies |
| Desalting | Salt removal | Quick, simple | No failure sequence removal | Pre-analysis cleanup |
| Size-Exclusion Chromatography | Size (molecular) separation | Gentle for large conjugates | Lower resolution for small impurities | Large or conjugated oligonucleotides |
| Ethanol/Acetone precipitation | Salt exchange and small molecule removal | Quick, simple | No failure sequence removal | Post-conjugation cleanup |
| Ultrafiltration | Size-based separation using membrane | Quick, simple | No failure sequence removal | Contaminant removal |
Rigorous characterization confirms molecular identity, quantifies purity, measures concentration, and assesses stability, forming the foundation for quality assurance and regulatory dossiers. Early impurity detection via orthogonal methods de-risks projects and ensures oligonucleotides perform reliably in biological assays or clinical development.
| Technique | Purpose |
| LC-MS | Confirms molecular weight & identity |
| HRMS | High-accuracy QC for modified Oligos |
| HPLC | Purity check post synthesis |
| UV | Concentration measurement |
| PAGE | Analytical purity for short oligonucleotides (Optional) |
| NMR | Structural confirmation (Optional) (For raw materials before synthesis start) |
Aragen also performs endotoxin testing using Charles River Endosafe® LAL cartridges for preclinical-grade oligos.
The ability to access high-quality, well-characterized phosphoramidites—combined with integrated oligonucleotide synthesis—directly accelerates client programs, minimizes chemistry risk, and supports increasingly complex molecular designs.
Enabling Innovation and Customization
Enabling innovation and customization in oligonucleotide development allows organizations to rapidly adapt synthesis platforms, analytical strategies, and modification chemistries to meet evolving therapeutic and research needs. Modern oligonucleotide programs increasingly require diverse sequence architectures—such as mixed-backbone designs, novel linkages, stereo defined phosphonothioates, conjugates, and specialty modifications—and innovation in chemistry, solid supports, and reagent formulations enables these capabilities.
Flexible synthesis systems, modular purification workflows, and data-driven analytics support rapid turnaround and high quality, while customization enables project-specific optimization in functional groups, scale, purity, and conjugation. By integrating modeling, automation, and real-time analytics, teams can accelerate design–make–test cycles and deliver high-performance oligonucleotides tailored to specialized biological, diagnostic, or therapeutic goals, strengthening development pipelines for future scientific and regulatory demands.
Aragen’s Oligonucleotide Innovation & Discovery Platform
Aragen’s phosphoramidite chemistry expertise enables discovery-driven oligonucleotide solutions for customers that enable innovation and accelerate research or therapeutic development. Here are some key approaches:
1. Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis
2. High-Throughput Screening & Discovery
3. Analytical& Characterization Service
4. Collaborative R&D Platforms
5. Small-Scale Route Scouting for Oligonucleotide Projects
Supports early-stage discovery and development.
This approach offers CRO customers fast turnaround to accelerate candidate selection, risk reduction by identifying optimal routes before scale-up, and cost savings through minimized early-phase waste, with deliverables including route comparison matrices, analytical data packages, and scale-up readiness recommendations.
Supporting Therapeutic and Diagnostic Modalities
Aragen’s phosphoramidite platforms support applications across:
De-Risking the Chemistry Supply Chain
End-to-end capability—spanning Oligonucleotides synthesis, purification, and QC—reduces supply chain complexity and shortens time-to-material. CRDMO integration, as embodied by Aragen’s model, eliminates fragmentation across vendors, ensuring uniform quality and faster delivery.
Deciding between in-house synthesis and outsourcing depends on long-term strategy, development timelines, and capability maturity.
In-House Synthesis
Enhancing In-House Capabilities Through CRDMO Collaboration
Partnerships with CRDMOs like Aragen act as an extension of a client’s R&D and production teams. Beyond manufacturing, these collaborations build process understanding, ensure regulatory alignment, and accelerate technology transfer.
Collaboration Benefits
Such partnerships enable organizations to strengthen internal competencies while maintaining high production reliability and scalability.
Phosphoramidite chemistry continues to drive the advancement of oligonucleotide therapeutics, diagnostics, and synthetic biology applications. Its combination of precision, scalability, and adaptability makes it the defining platform for nucleic acid synthesis.
Through integrated process innovation, sustainability measures, and analytical excellence, CRDMOs like Aragen are enabling faster, cleaner, and more reproducible oligonucleotide manufacturing. This technology partnership not only expedites lab-to-clinic transitions but also fuels innovation at every stage—from molecular design to regulatory submission and commercial supply.
