

As the global nutraceutical industry grows rapidly, regulatory scrutiny by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is rising to protect consumers and ensure market integrity. Developers of dietary supplements, functional foods, and botanical ingredients must conduct evidence-based, transparent, and well-documented toxicology assessments to meet FDA and EFSA expectations.
Furthermore, the integration of computational toxicology, in silico modeling, and high-throughput screening technologies is transforming safety evaluations. These tools not only reduce reliance on animal testing but also offer predictive insights into ingredient behavior, enhancing regulatory confidence and ethical standards. The convergence of toxicology with data science and artificial intelligence (AI) is also expected to streamline risk assessments and regulatory submissions.
This whitepaper details how modern toxicology—moving beyond reliance on animal models—employs New Approach Methodologies (NAMs) and harmonized global strategies to enable market access, build consumer trust, and accelerate innovation.
Nutraceuticals today encompass an ever-growing variety of ingredients including plant extracts, bioactive peptides, fermented products, and novel micronutrients. Many of these are new to the market and lack a substantial history of safe human use, meaning toxicology data becomes a critical aspect of their regulatory dossiers.
In the U.S., ingredients classified as New Dietary Ingredients (NDIs) must be notified to the FDA prior to marketing. This requires:
In the European Union, the Novel Food Regulation (EU 2015/2283) governs many new nutraceutical components mandating:
For both regions, the quality, relevance, and scientific rigor of toxicology data are critical factors influencing regulatory approval, commercial success, and liability mitigation.
Meeting FDA and EFSA safety expectations requires targeted toxicological data demonstrating that nutraceutical ingredients are safe under realistic use conditions. Below are the core toxicology endpoints, their purpose, and the specific regulatory requirements in both the U.S. and EU (Table 1).
Table 1: FDA vs EFSA regulatory requirements for safety assessment of nutraceutical ingredients.
| Endpoint | Purpose in Toxicology Assessment | FDA Requirement | EFSA Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genotoxicity | Detects potential DNA damage and mutation risk | AMES test and micronucleus test required | AMES and in vitro micronucleus tests are initial screens; if positive, follow up with in vivo micronucleus, comet assay, or transgenic rodent mutation assay |
| Sub-chronic Toxicity | Identifies target organ/systemic toxicity; establishes safe intake levels after repeated exposure (28 or 90 days). | 28- or 90-day animal studies, duration based on exposure | Mandatory 90-day studies in rodents for most novel foods |
| ADME Studies | Determines Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME), crucial for understanding systemic exposure and accumulation | Case-by-case, not always required | Strongly encouraged for novel foods and new ingredients |
| Reproductive Toxicity | Evaluates risk to fertility, pregnancy, and offspring development—critical when wide population exposure is possible | Required for broad exposure or sensitive populations | Required when ingredients may be consumed by general/sensitive population |
| Carcinogenicity | Assesses risk of cancer after long-term or lifetime exposure; informs safe use and labeling | Required based on structural or exposure-based concern | Required for ingredients intended for long-term exposure |
A well-designed toxicology program addresses these core endpoints as dictated by regulatory agencies. Satisfying both FDA and EFSA requirements with properly scoped studies and documentation not only enables regulatory approval but also helps build consumer confidence and minimizes post-market risk.
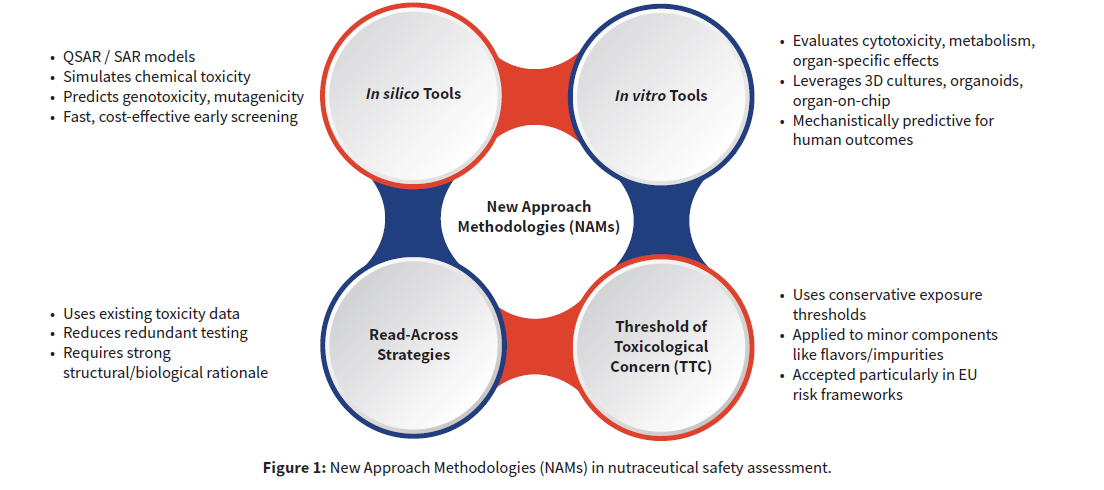
A reliable toxicology assessment is built on traditional methods—hazard identification, risk characterization, and, when appropriate, targeted in vivo validation. Besides these, modern assessments like New Approach Methodologies (NAMs) are strategically combined with traditional methods to achieve more human-relevant and efficient safety insights. The use of tiered tests, along with tailored data generation for risk assessment, provides a pragmatic and effective strategy for safety assessment.
Hazard Identification
In Vivo Validation
Integration of NAMs
Risk Characterization and Dossier Compilation
Regulators around the world are actively encouraging the use of NAMs where scientifically justified, recognizing their value in improving ethical standards while maintaining rigorous safety evaluation. By thoughtfully integrating NAMs with traditional studies, the toxicology program becomes more efficient, ethical, and scientifically powerful. Effective use of NAMs:
Additionally, several strategic considerations and emerging tools can further enhance the rigor and regulatory success of toxicology assessments:
Seamless integration of NAMs across all stages of toxicological assessment—from hazard identification through risk characterization— ensures their full potential is realized.
While safety is the mutual priority, differences in regulatory philosophies drive distinct submission expectations:
Given these differences, it is critical to design toxicology programs that satisfy both authorities upfront, facilitating faster global commercialization. To unlock both U.S. and EU markets efficiently:
Early consultation with experienced toxicology and regulatory experts is recommended to tailor study design and data packages accordingly.
Innovation in nutraceuticals must be underpinned by rigorous safety evaluation aligned with FDA and EFSA guidelines. By combining classical toxicology with innovative NAMs and adopting a globally harmonized regulatory strategy, companies can accelerate time to market, reduce regulatory risk, and foster consumer trust.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, proactive engagement with authorities, transparent communication of scientific rationale, and continuous investment in safety science will be key to sustaining innovation and public confidence in nutraceuticals.
Companies that embed safety-by-design principles early in product development—integrating toxicology, formulation science, and regulatory foresight—are better positioned to lead in a competitive and compliance-driven market.
Launching new nutraceutical ingredients demands more than innovation—it requires scientific rigor and regulatory precision. At INTOX, an Aragen company, we specialize in comprehensive toxicology services that align with global regulatory expectations, including FDA and EFSA standards.
Our expertise covers all stages—from study design and execution to data analysis and regulatory submissions. Whether pursuing GRAS status, NDI notification, or EFSA novel food approval, INTOX ensures your safety data meets the highest scientific and compliance standards. INTOX has successfully conducted multiple studies that have supported regulatory approvals for the various NDI or food additives.
